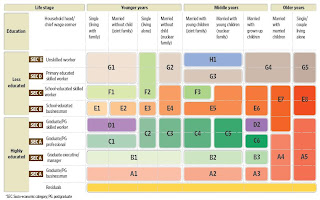
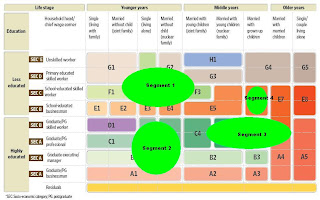
Today I attempt to list down the categories and dimension which could be input into a customer segmentation model. This list, though comprehensive, is in no way exhaustive. But I don't think this is an area of concern since not many companies could fill in a majority of these dimensions with customer data.
I have categorised the dimension into classes. For some dimension, I have also stated some sample values. I am not attempting to explain the dimension since a quick google on the meaning of the dimension name should give enough insight into its explanation and the likely values the dimension with contain in the data set.
1. Class: Geographic
1.a: Region
1.b: City size
1.c: Density of area
1.d: Climate
2. Class: Demographic
2.a: Age
2.b: Sex
2.c: Marital status
2.d: Income
2.e: Education
2.f: Occupation
3. Class: Psychological
3.a: Needs-motivation
sample values: shelter, safety, security, affection, sense of self worth
3.b: Personality
sample values: extroverts, novelty seeker, aggressives, low dogmatics
3.c: Perception
sample values: low-risk, moderate-risk, high-risk
3.d: Learning involvement
3.e: Attitudes
4. Class: Pscychographic
4.a: Lifestyle
sample values: economy-minded, couch potatoes, outdoor enthusiasts, status seekers
5. Class: Sociocultural
5.a: Cultures
sample values: Bangla, Egyptian, Indian, Nepali, Pakistani
5.b: Religion
5.c: Subcultures
sample values: African, American, Asian, Hispanic
5.d: Social Class
5.e: Family life cycle
sample values: bachelors, young married, full nesters, empty nesters
6. Class: Use related
6.a: Usage rate
sample values: heavy users, medium users, light users, non users
6.b: Awareness status
sample values: unaware, aware, interested, enthusiastic
6.c: Brand loyalty
sample values: none, some, strong
7. Class: Use situation
7.a: Time
sample values: leisure, work, rush, morning, night
7.b: Objective
sample values: personal, gift, snack, fun, achievement
7.c: Location
sample values: home, work, friend's home, in-store
7.d: Person
sample values: self, family members, friends, supervisor, manager, peers
8. Class: Benefit
sample values: convenience, social accpetance, long lasting, economy, value-for-money
9. Class: Hybrid segmentation: implies using output of other segmentation model as an input to the current segmentation exercise.
Contact me at michaeldsilva@gmail.com if you want to discuss further on conducting a segmentation exercise for your customer base.